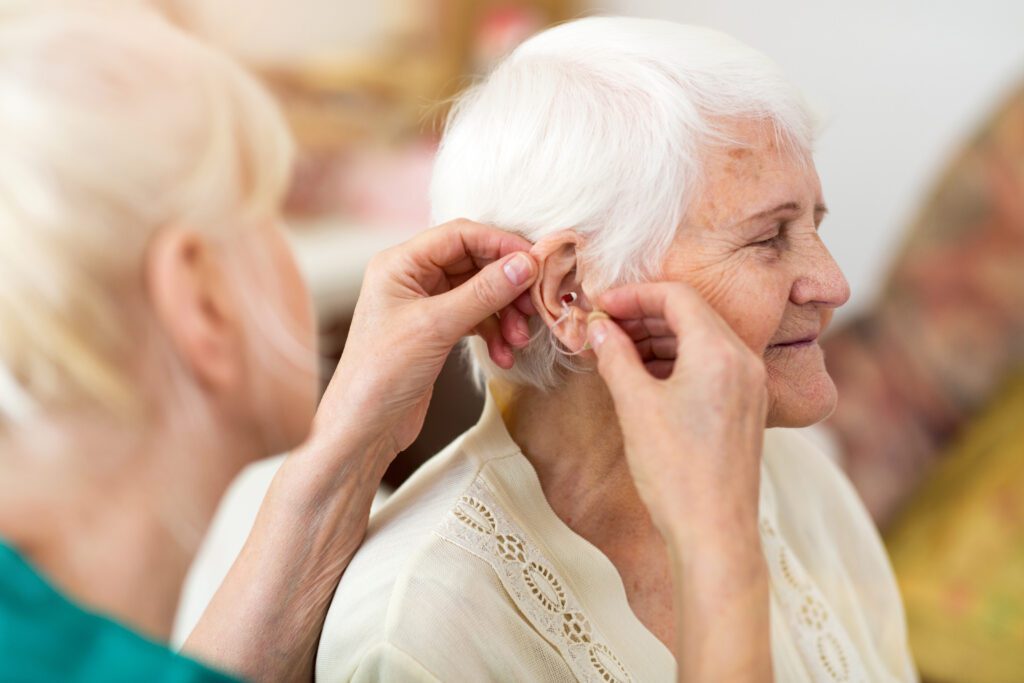
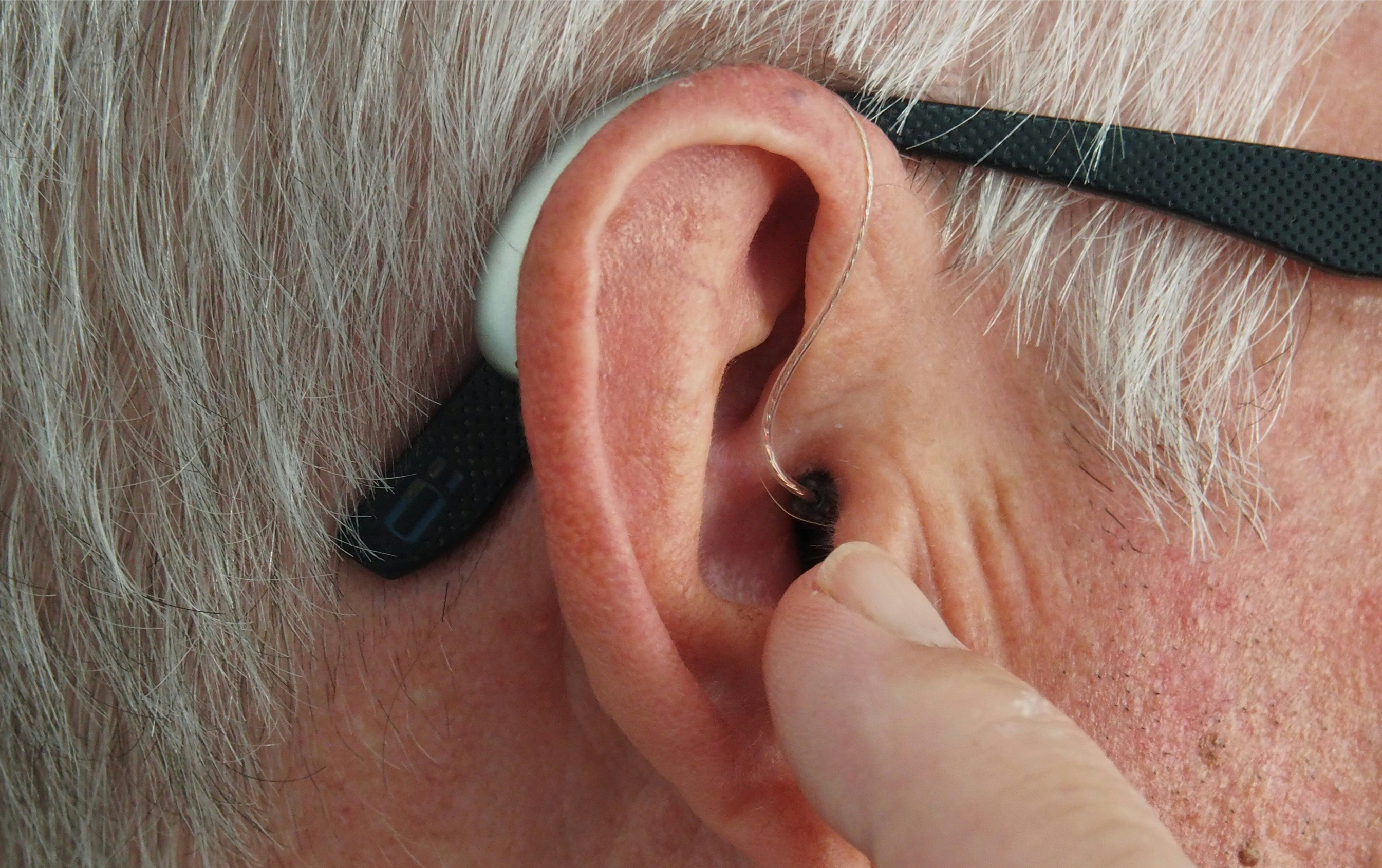
Proper maintenance and care of your hearing aid are crucial for ensuring its performance and longevity. Whether you are a first-time user or have been using hearing aids for years, following these comprehensive tips will help you maintain your device effectively.
Understanding the Importance of Hearing Aid Care
Hearing aids are sophisticated electronic devices that require regular upkeep to function at their best. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced performance, shorter lifespan, and potentially costly repairs. By establishing a routine care regimen, you can ensure that your hearing aids provide the best possible hearing experience.
Daily Care and Cleaning
- Clean Your Hearing Aids Regularly
Daily cleaning is vital to prevent the buildup of earwax, dirt, and oils, which can clog the hearing aid’s components. Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe the exterior of the hearing aid, paying special attention to the earmold and ear dome. For more thorough cleaning, use a soft brush designed for hearing aids to gently remove any debris.
- Avoid Moisture and Water
Hearing aids are sensitive to moisture. Remove your hearing aids before showering, swimming, or engaging in any activities that may expose them to water. Even high humidity environments can be harmful. Consider investing in a dehumidifier specifically designed for hearing aids to store them overnight, which helps to remove any accumulated moisture.
Battery Care and Management
- Proper Battery Handling
Batteries are the lifeline of your hearing aid. Replace them regularly and carry spare batteries with you. Before inserting a new battery, clean the battery contacts in the hearing aid with a dry cloth. Ensure that you are using the correct type and size of battery recommended by the manufacturer.
- Battery Storage
When not in use, remove the batteries to prevent corrosion. Store the batteries in a cool, dry place, and avoid letting the terminals touch each other to prevent short-circuiting.
Preventing Physical Damage
- Protect Against Drops and Impacts
Hearing aids are delicate devices. Always handle them with care to avoid drops and impacts. When inserting or removing your hearing aids, do so over a soft surface like a bed or a sofa to cushion any accidental drops.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Extreme temperatures can damage the electronic components of your hearing aids. Do not leave them in direct sunlight, near a heater, or in a very cold place. Sudden temperature changes can also cause condensation, leading to moisture damage.
Professional Maintenance and Check-Ups
- Regular Professional Check-Ups
Schedule regular appointments with your hearing care professional for maintenance and performance checks. Professionals can perform deep cleaning, make necessary adjustments, and identify any potential issues before they become major problems.
- Use Professional Cleaning Kits
Invest in cleaning kits specifically designed for hearing aids. These kits often include tools like wax removal brushes, tube cleaners, and air blowers that can help maintain your device without causing damage.
Tips for Specific Hearing Aid Types
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids
For BTE hearing aids, regularly check and clean the tubing. Replace the tubing if it becomes stiff or discolored. Ensure that the earmold is free of earwax and moisture.
- In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids
ITE hearing aids have components that sit directly in the ear canal, making them more susceptible to earwax buildup. Clean the microphone and receiver ports carefully, and consider using a wax guard to protect these openings.
Additional Tips
- Avoid Using Harsh Chemicals
Never use household cleaning agents, alcohol, or solvents on your hearing aids. These substances can damage the casing and internal components. Use only products recommended by your hearing care provider.
- Handle with Clean Hands
Always wash and dry your hands before handling your hearing aids. This prevents the transfer of oils, dirt, and moisture.
- Monitor Performance
Be aware of any changes in your hearing aid’s performance, such as reduced sound quality or feedback. These changes can indicate that the device needs cleaning, new batteries, or professional servicing.
Proper care and maintenance of your hearing aid are essential for ensuring its optimal performance and longevity. By incorporating these daily, weekly, and professional care routines, you can protect your investment and enjoy clear, reliable hearing. If you have any concerns or notice any issues with your hearing aid, do not hesitate to contact your hearing care professional for advice and support.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your hearing aids remain in excellent condition, providing you with the best possible hearing experience for years to come.